By Lars Jensen
Stop Trusting Databases. Start Trusting the Chain.
Most “crypto casinos” are essentially traditional web 2.0 sites that happen to accept Bitcoin. You deposit funds, your money goes into their hot wallet, and your balance is updated on a private SQL database. You are trusting them not to freeze your account. You are trusting them to honor your withdrawal. In 2026, that is not good enough.
Enter Decentralized Casinos (dApps). These platforms do not hold your money. They do not ask for your passport. They operate entirely on smart contracts—self-executing code stored on the blockchain. If the code says you won, the payout is automatic. No manager can veto it.
As a blockchain architect, I advocate for “Trustless” systems. This guide dissects the mechanics of on-chain gambling, how to audit a liquidity pool, and why Web3 betting is the only true form of financial freedom in the gambling sector.
In this Article:
The Architecture: Centralized vs. Decentralized
To understand the security benefit, you must understand the flow of funds.
Centralized Crypto Casinos (Custodial)
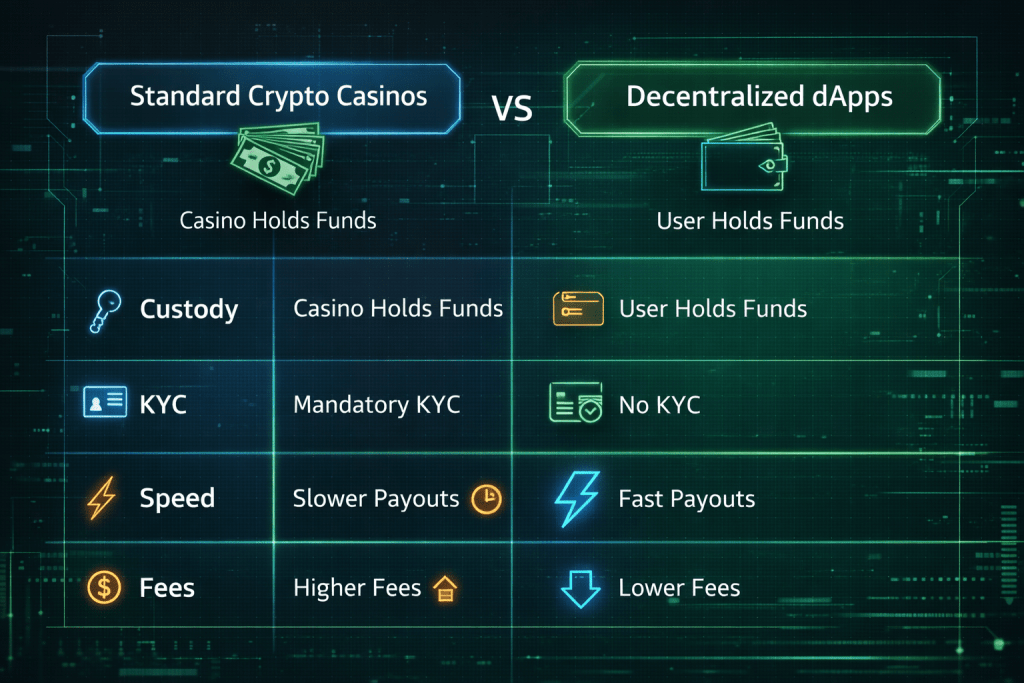
In a standard crypto casino, you send 1 BTC to a deposit address. The casino now has custody of that 1 BTC. You see a number on a screen, but that number is just a database entry. If their server goes down or they get hacked, your money is gone. This is the “Not your keys, not your coins” problem.
Decentralized Casinos (Non-Custodial)
In a decentralized casino, you connect your Web3 wallet (like MetaMask or Phantom). When you place a bet, you are signing a transaction that interacts directly with a Smart Contract. The funds move from your wallet to the contract’s escrow. The contract executes the game logic (using an Oracle for randomness). If you win, the contract immediately sends funds back to your wallet.
The casino never holds your funds. The code holds them.
Smart Contracts and The Liquidity Pool
A decentralized casino does not have a bank account. It has a Liquidity Pool (LP). This is a pot of tokens crowdsourced from investors who stake their crypto to bankroll the house.
When you win, you are paid directly from this smart contract pool. This introduces a critical concept: Max Payout Verification.
Before you play, you can read the contract on Etherscan or Solscan. You can see exactly how much money is in the liquidity pool. If the pool holds 100 ETH, the contract mathematically cannot pay out a jackpot of 200 ETH. In traditional casinos, you have to guess if they are solvent. In decentralized casinos, solvency is public record.
The Randomness Problem: VRF on the Blockchain
Blockchains are deterministic. This means if you replay the history, you get the same result. This makes generating random numbers (RNG) difficult natively on-chain. If a miner knows the block hash ahead of time, they could predict the outcome of your dice roll.
To solve this, legitimate decentralized casinos use Chainlink VRF (Verifiable Random Function).
- Request: The smart contract requests a random number.
- Generation: Chainlink generates a random number and a cryptographic proof off-chain.
- Verification: The smart contract verifies the proof on-chain before accepting the number.
If a dApp does not use an Oracle like Chainlink or a commit-reveal scheme, it is vulnerable to “Front-Running” attacks by miners or validators.
Pros and Cons of Web3 Gambling
Decentralization is secure, but it is not always fast. Here is the technical trade-off:
The Advantages
- Immutable Payouts: Smart contracts execute automatically. No “pending withdrawal” delays.
- Anonymity: No sign-ups. No KYC documents. You are just a wallet address.
- Transparency: Every bet, win, and loss is a permanent transaction on the blockchain.
The Bottlenecks
- Gas Fees: Every bet is a transaction. On Ethereum, this is too expensive. This is why most dApps run on Polygon, Solana, or Arbitrum.
- Speed: You must wait for block confirmation. It is slower than the instant feedback of a centralized database.
- User Responsibility: If you lose your private keys, there is no “Forgot Password” button. Your funds are unrecoverable.
How to Audit a dApp Before Connecting
Never connect your main wallet to a new dApp without checking the basics. Here is my security checklist:
- Contract Verification: Go to the block explorer (e.g., Etherscan). Is the contract source code verified (green checkmark)? If the code is unverified, do not touch it.
- Audit Reports: Has the code been audited by firms like CertiK or Hacken? Look for the audit PDF in their footer.
- Token Approvals: When you approve a token, check the limit. Malicious contracts ask for “Unlimited Spend” allowance. Use tools like Revoke.cash to manage permissions.
- Liquidity Lock: Check if the developers have locked the liquidity. If not, they could pull the funds (Rug Pull) at any moment.
Conclusion: The Era of Self-Custody
The future of gambling is not asking for permission to withdraw your own money. Decentralized casinos represent a shift from “Don’t be Evil” (hoping the casino is nice) to “Can’t be Evil” (mathematically preventing them from cheating). It requires more technical knowledge, but the security of knowing the House cannot freeze your assets is worth the learning curve.
FAQ: Decentralized Gambling
Do I need VPN for decentralized casinos?
Technically, dApps live on the blockchain, which has no borders. However, the website interface (frontend) may block certain IPs (Geo-blocking). While the smart contract itself cannot block you, users often use VPNs to access the frontend interface.
What is “Gas” in crypto gambling?
Gas is the transaction fee paid to network validators. If you play on a decentralized casino, you pay a small gas fee for every bet or session. Chains like Solana or BSC have negligible fees (fractions of a cent), making them ideal for high-volume betting.
Can a smart contract be hacked?
Yes. If there is a bug in the code, hackers can drain the liquidity pool. This is why you should only play on platforms with audited contracts and a long track record. Security in Web3 is about code quality, not physical vaults.
How do I deposit?
You don’t “deposit” in the traditional sense. You simply connect your wallet. Your funds stay in your wallet until the moment you sign the transaction to bet. There is no account balance on the site, only your wallet balance.
What is the difference between a dApp and a Provably Fair site?
A standard Provably Fair site (like Stake or BC.Game) is still centralized; they hold your money. A dApp is decentralized; nobody holds your money but you. dApps are inherently Provably Fair because the entire logic is visible on-chain.